# Notes
# Best programming practices
# What is a program
A program is a sequence of instructions that specifies how to perform a computation. The computation might be something mathematical, such as solving a system of mathematical equations or finding the roots of a polynomial, but it can also be a symbolic computation, such as searching and replacing text in a document or something graphical, like processing user input on an ATM device.
# Essence or "Workflow" of a Program
graph LR | |
A[A list of positive number] --> |Input|B(Progress <br> find the largest number of the list) | |
B --> |Output|C[A single number] |
- input
- Get data from the "outside world". This might be reading data from the keyboard or a file, or even some kind of sensor like a microphone or GPS.
- process
- Perform computions by the CPU (Central Processing Unit) of the device
- output
- Display the results of the program on a screen or store them in a file or perhaps write them to a device like a speaker to play music or speak text.
# Design Aspects for problem solving

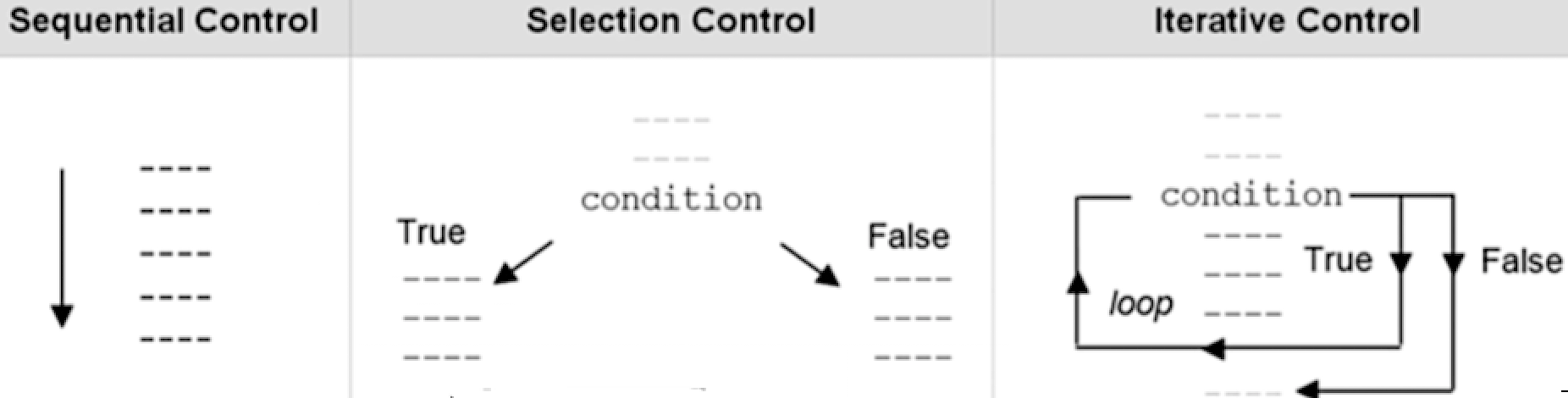
# Basic Building Block of a Program
Every program goes thru either or all of the following flows
- Sequential (Top Down execution)
- Selective (Decision making execution)
- Iterative or "Loop repetition"
# Java Fundamentals
# Variables
Defined: a value stored in memory that can change
Declarations
Establish good naming conventions!Ex.
emp_RateorempRateempHours,empIdScope (variable visibility)
Variables can be defined to be "visible" or seen at the local vs. class level (static).
# Constants
Defined: a value stored in memory that cannot change
Use of keyword -> final
final int ival = 20; //value needed immediately upon declaration! |
# Basic Data Types
| Primitives (8) | Reference or Class based examples |
|---|---|
| byte | Random |
| boolean | String |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
| int | Integer |
| short | Short |
| long | Long |
| char | Character |
int j=0, k=1; | |
double a = 2.0; | |
double b = 5; |
Avoid a common pitfall!
int result = 3/4; //0 as truncation occurs |
# Operators
Know operator precedence and associativities!
Order of operations (highest to lowest)
- Arithmetic
- Conditionals
(and&&, or||, not!) - Relational (
>,<,>=,<=,!=,==)
Keynote: use shortcut operators in assignment statements
++count; //pre increment operator (change to variable takes place immediately) | |
// vs. | |
count++; //post increment operator (change to variable takes place after assignment ends) | |
// same as | |
count = count + 1; | |
// or | |
count+=1; |
Avoid a common pitfall! -Checking for equality!!
FOR NUMERIC TYPES USE
int a = 12; | |
(5 == a) |
FOR STRING TYPES USE EQUALS METHOD!
String name1 = "Joe", name2 = "Jack"; | |
(name1.equals(name2)) |
# Conditionals
# if statements
format:
if(a>b) | |
//if true do something | |
else | |
//if false do something else |
Make use of curly bracies { } to combine statements
if(a>b) { | |
result = a; | |
System.out.print("Value = " + result); | |
} | |
else { | |
result = b; | |
System.out.print("Value = " + result); | |
} |
# Other forms- multi branched, nested
if alternative – the CEO (Conditional Expression Operator)
Known as a ternary operator - ? :
format: conditon ? true expression : false expression
int result = a>b ? a : b; | |
// if statement equivalent | |
if(a>b) | |
result = a; | |
else | |
result = b; |
# Truth tables
And && Expression- a>b && b>c | Or || Expression- a>b || b>c | Not ! Expression- !(a>b) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cond. | Result | Cond. | Result | ^^ | |
T && T | T | T || T | T | !T = F | |
F && T | F | F || T | T | !F= T | |
T && F | F | T || F | T | ||
F && F | F | F || F | F | ||
# Loops
while, do-while, for, for enhanced
format: while (some condition holds true)
int count = 0; | |
while (count<10) { | |
//do something | |
count++; //increment counter variable | |
} |
# Arrays
Index or subscript based
Holds a series or list of values
Can be fixed or dynamic
Chief advantages
Can be sorted, searched, averaged, find max/min values, printed…Any disadvantages???
int array[] = {1,2,3,4,5}; | |
array[2]=14; //update array at subscript 2, element #3 |
| Element number | Subscript number (or index) | Value at subscript position |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 3 | 2 | 14 |
| 4 | 3 | 4 |
| 5 | 4 | 5 |
Ex. Cycle thru array up to array length - 1
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) | |
System.out.print(array[i] + " "); |
# Review
# True/False
The first step to the problem-solving process is to implement the algorithm in a programming language, such as Java, and verify that the algorithm works.
译:解决问题过程的第一步是用一种编程语言(例如 Java)实现该算法,并验证该算法是否有效。
- Define Problem 定义问题
- Create (suggest) a solution (s) 创建一个解决方案
- Code away!! 编写代码
- Test 测试
- Maintenance (ongoing) (持续)维护
The symbol
'5'does not belong to the char data type because 5 is a digit.char letter = 'a';
String letter = "a";If
++xis used in an expression, first the expression is evaluated, and then the value ofxis incremented by1.++x;same as =>x = x + 1;++x;(先加再运算)x = x + 1;(update to variable occurs AFTER expression is evalutated 对变量的更新发生在表达式被赋值之后)In Java,
!,&&, and||are called logical operators.- Arithmetic 算数
- Conditional 条件
- Relational 关系
Suppose
PandQare logical expressions. The logical expressionP && Qis false if bothPandQare false.Ex.
P=>A>B,Q=>A==2isP&&Qa true outcomeThe output of the Java code, assuming that all variables are properly declared, is 32.
num = 10;
while (num <= 32)
num = num + 5;
System.out.println(num);
Result:
15 20 25 30 35
Ending value is 35A constructor has no type and is therefore a void method.
译:构造函数没有类型,因此是一个空方法。
PURPOSE: SET THE OBJECT(S) TO AN INITIAL STATE.
目的:将对象设置为初始状态。
构造函数没有 返回类型,所以没有 void。Given the declaration
double[] numList = new double[20]; //0-19 INDICIE
the statement
numList[12] = numList[5] + numList[7];
updates the content of the thirteenth component of the array numList.
A subclass can override
publicmethods of a superclass.子类可以重写父类的方法
If an exception occurs in a try block and that exception is caught by a catch block, then the remaining catch blocks associated with that try block are ignored.
如果在一个 try 块中发生异常,并且该异常被 catch 块捕获,那么与该 try 块关联的其余 catch 块将被忽略。
# Multiple Choice
To develop a program to solve a problem, you start by .
The first step in OOD is to identify the components called .
OOD:Object-Oriented Design,即面向对象设计
Which of the following is a valid int value?
For letter b response above, you can include a character like a comma ( , ) to be stored as a numeric value
For letter c response above, you can't include a decimal ( . ) to be stored as a 'int' numeric value
For letter d response above, the value is too large to be stored as an 'int'. Try coding the variable with that value as an assignment and see the error message.Which of the following is a valid statement?
(i)
int num = new int(67);
(ii)String name = new ("Doe");
(iii)String name = "Doe";Syntax for ( i ) is invalid. Type should be Integer not 'int' when creating an integer type object
Syntax for ( ii ) s/b String name = new String ("Doe");Declaring a class level variable as static means .
将类声明为静态意味着什么?
Consider the following statements.
double x;
String y;
y = String.format("%.2f", x);
If
x = 285.679, what is the value of y?保留两位小数
What is the output of the following Java code?
int x = 0;
if (x > 0)
System.out.println("positive ");
System.out.println("zero ");
System.out.println("negative");
Notice that the second statement although aligned under the
ifstatement namelySystem.out.println("zero ");executes no matter what as theifstatement has no braces{ }to encompass the 2ndprintlnstatement.
尽管第二个语句System.out.println("zero ");与if语句对齐,但if语句没有用大括号{}将第二个println语句括起来,因此它总是会被执行。
For the executions using the compareTo built-in java method that follows (questions 18-20), outcomes are basically as follows
If str1 > str2 when comparing characters from (left to right each time) the outcome will be some positive number result
If str1 < str2 when comparing characters from (left to right each time) the outcome will be some negative number result
If str1 == str2 when comparing characters from (left to right each time) the outcome will be 0.Comparisons like the above are good when sorting data.
If str1 is "Hello" and str2 is "Hi", which of the following could be a result of
str1.compareTo(str2);?Here when comparing
H e l l o with
H i
Theeand theiwhen comparing characters from each string from left to right show a lexographical difference of 4 characters.
As str1 > str2, a negative result appears by a distance of 4 characters yielding a -4.If str1 is "Hello" and str2 is "Hi", which of the following could be a result of
str2.compareTo(str1);?Here similarly to question 18 result there is a difference of 4 characters, yielding a positive 4 as str2 is greater than str1.
If str1 is "Hello" and str2 is "Hello", which of the following could be a result of
str1.compareTo(str2);?Here comparisons between string values (characters) are equal, hence the 0 outcome.