# Different from PCs or web
- Immediate requests
立即要求 - Short interactions, frequently interrupted
互动简短,经常被打断 - Public use
公共用途 - Fashion statement
时尚宣言- Less business-oriented
较少以业务为导向 - More value to design
更具设计价值
- Less business-oriented
- Little engagement
很少参与 - Must always be able to answer the phone
必须始终能够接听电话
# Mobile first
Consultants recommend web sites designed for mobile first
建议为移动设备优先设计的网站
- Understand users' most important tasks
了解用户最重要的任务 - Focus on key elements
专注于关键要素 - Harder to get a good user experience
难以获得良好的用户体验 - Easier to spread out and add menu items, etc. versus removing them
与删除菜单项相比,更易于展开和添加菜单项等 - More demands on responsiveness
对响应能力的更多要求 - Interaction limitations –no hover capability
互动限制 - 不要悬停功能
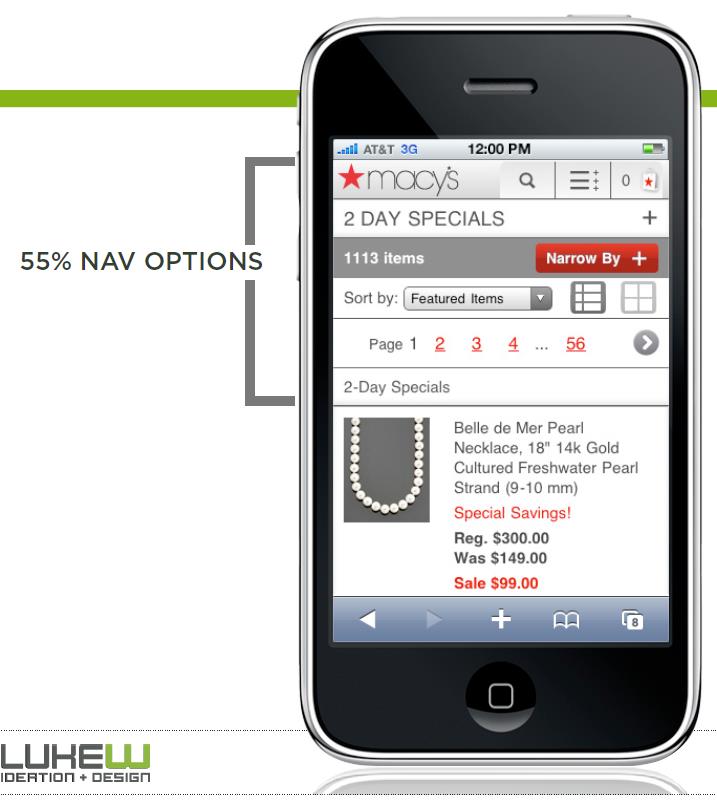
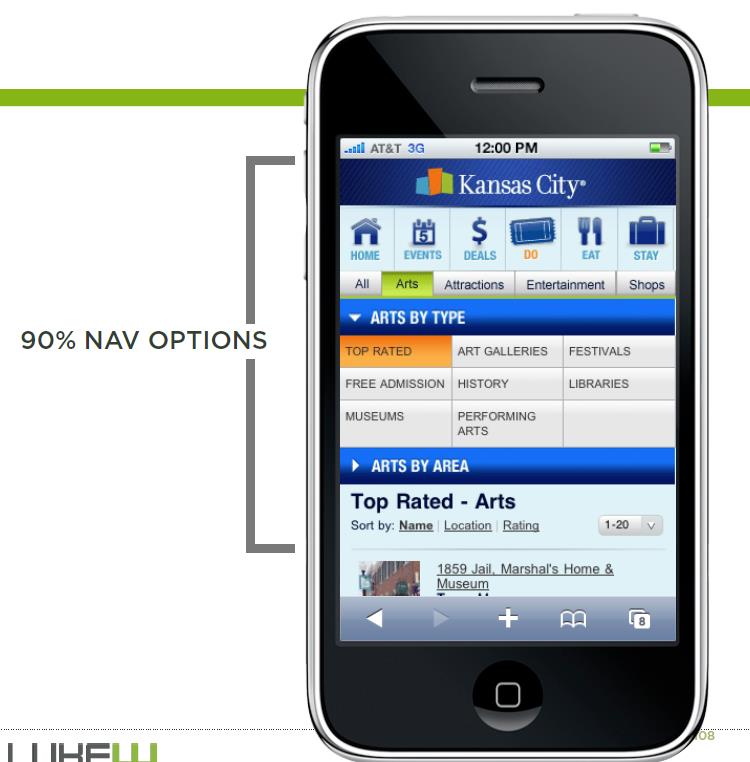
# Focus on navigation or content
# Responsive Design 响应式设计
- Web sites adjust themselves based on size of screen
网站会根据屏幕大小自行调整 - Programmed into the html of each page
编程到每个页面的 html 中- Mobile vs. desktop versions
移动版与台式机版 - Vs. providing different pages based on browser/device request
Vs. 根据浏览器 / 设备请求提供不同的页面
- Mobile vs. desktop versions
- Html and CSS have built-in features
HTML 和 CSS 内置有响应式功能 - Dreamweaver, etc. let you design for different ranges of sizes
Dreamweaver 等可让您设计不同的尺寸范围 - Fewer options & elements (faster downloading)
更少的选项和元素(更快的下载) - Designed for smaller screen
专为较小的屏幕而设计 - Responsive design works better for search-engine optimization (SEO)
自适应设计更适合搜索引擎优化(SEO)
pc 版和移动版可以使用同一个 URL 地址
# Human abilities
Human considered to be a…
人类被认为是……
Sensory processor
感官处理器- Experimental psych, sensory psych
实验心理,感觉心理 - e.g. Model--Human Processor (Card, Moran & Newell)
模型 - 人为处理器
- Experimental psych, sensory psych
Interpreter/Predictor
解释器 / 预测器- Cognitive psych, AI
认知心理,人工智能 - e.g. Distributed cognition (Hutchins)
分布式认知
- Cognitive psych, AI
Actor in environment
环境中的活动者- Activity theory, ethnography
活动理论,人种志 - e.g. Situated action (Suchman)
情景动作 - e.g. Activity theory (Vygotsky, Nardi)
活动理论
- Activity theory, ethnography
# What makes a system usable
Human Considered to be a .. | Usability results when the system .. | Evaluation methods.. |
|---|---|---|
Sensory Processor | Fits within human limits | Quantitative Experiments |
Interpretor/Predictor | Fits with knowledge | Task Analysis,Contextual Inquiry |
Actor in environment | Fits with task and social context | Ethnographic field work, Participatory design |
# Two views of interaction
互动的两种观点
- Interaction with
- Software system is a tool or machine
软件系统是工具还是机器 - Interface is a usability--engineered membrane
界面是易用性 - 工程膜 - Human as processor and Interpreter models
人作为处理器和解释器模型
- Software system is a tool or machine
- Interaction through
通过互动- Software as a medium used to interact with task object and other people
软件作为媒介,与任务对象及其他人进行互动 - Interface plays a role in social context
界面在社交环境中发挥作用 - Human as interpreter and actor
人作为解释器和活动者
- Software as a medium used to interact with task object and other people
# Human capabilities
Senses | Information Processing | Motor Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Vision | Perceptual | Physical abilities |
| Hearing | Cognitive | Reach |
| Touch | Memory | Speed |
| Smell | -Short Term | |
| Taste | -Medium Term | |
| -Long Term | ||
| Processes | ||
| -Selective attention | ||
| -Learning | ||
| -Problem Solving | ||
| -Language |
# Senses
- Sight, Hearing, Touch important for current HCI.
视觉,听觉,触觉对于当前的人机交互非常重要。- Smell, Taste ???
闻起来,味道???
- Smell, Taste ???
- Abilities and limitations affect design
能力和局限性影响设计
Key concepts of senses:
感官的关键概念
- Just noticeable differences
只是明显的差异- How much of a change in stimulus is needed before it can be sensed
需要多少刺激才能感测到 - Tends to be logarithmic – Weber's law
倾向于对数 - 韦伯定律
- How much of a change in stimulus is needed before it can be sensed
- Magnitude of physical stimulus vs perceived magnitude
物理刺激的幅度与感知的幅度- Doubling number of photons does not double perceived intensity
光子数量加倍不会使感知强度加倍
- Doubling number of photons does not double perceived intensity
# Weber's law
Video: Weber's law and thresholds
# Vision
- Visual System
视觉系统- Eye 眼睛
- Retina 视网膜
- Neural Pathway 神经通路
- About 180º of arc 约 180º 弧度
- Light reception happens in retina (back of eye)
光接收发生在视网膜(眼后) - Fovea (highest-resolution area)
中央凹(最高分辨率区域) - Just 2º of arc
仅 2º 弧度 - 75% of visual operations
视觉操作的 75% - Not like a camera; doesn’t take the whole picture at once
不像照相机; 不能一次拍摄全部照片
# Visual abilities
Sensitivity 灵敏度
- Luminance 10 –107 ml (miliambert)
亮度 10 –107 毫升
- Luminance 10 –107 ml (miliambert)
Acuity 敏锐度
- Detection, Alignment, Recognition
检测,对准,识别 - Retinal position –Fovea has best acuity
视网膜位置–视力最强
- Detection, Alignment, Recognition
Movement 运动
- Tracking, Reading, Vibrations
跟踪,阅读,振动
- Tracking, Reading, Vibrations
Implications 含义
- Font size and location depend on task
字体大小和位置取决于任务 - Much done by context and grouping
通过情景和分组来完成很多工作
- Font size and location depend on task
Retina has 视网膜有
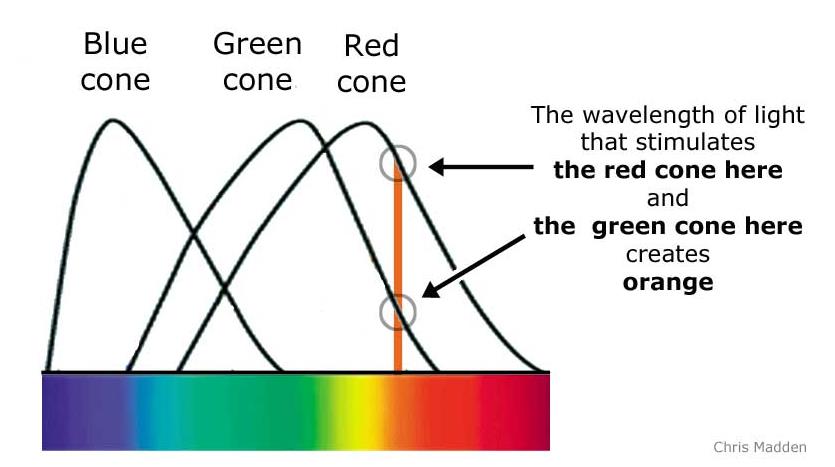
- 6.5 M cones (color vision), mostly at the fovea
6.5 M 视锥细胞(彩色视觉),主要在中央凹处 - About 150,000 cones per square millimeter
每平方毫米约 150,000 个圆锥 - Fewer blue sensing cones than red and green at the fovea
中央凹处的蓝色感应锥体比红色和绿色少 - 100 M rods (night vision), spread over the retina –none at the fovea
100 M 杆(夜视),散布在视网膜上–中央凹处无
- 6.5 M cones (color vision), mostly at the fovea
Adaptation 适应
Switching between dark and light causes fatigue
在黑暗和明亮之间切换会导致疲劳
# Color vision
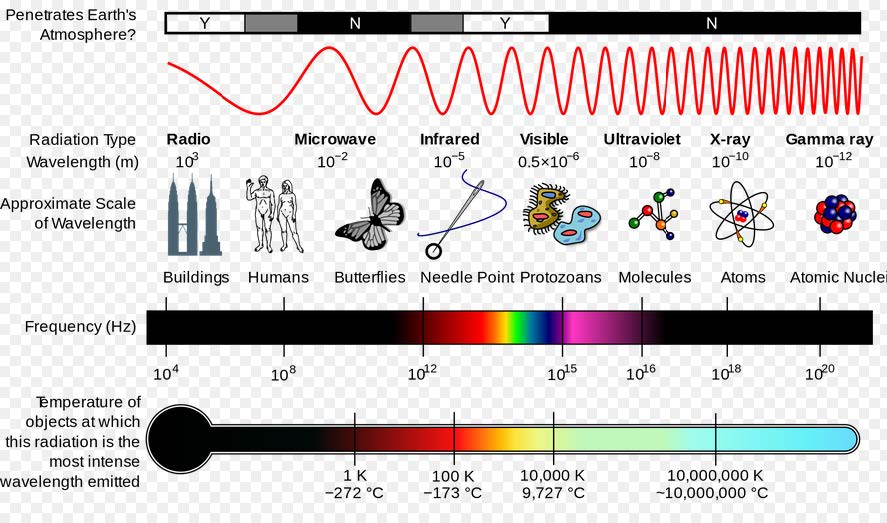
- Color and the retina
- 380nm (blue) ~ 770nm (red)
- Problems with cones or ganglion cells causes problems with color perception
- (Not really "color blindness")
- 8% males, 0.5% females
- Implications 含义
- Avoid saturated colors 避免色彩饱和
- Color coding should be redundant when possible 颜色编码应尽可能冗余
# Paul Morris Fitts's Law
- The bigger an object and the closer it is to us, the easier it is to move to.
物体越大,离我们越近,移动起来就越容易。- Fitts's law can be used as an aid to make educated decisions on the size and placement of user interface elements.
菲茨定律可以帮助做出有关用户界面元素的大小和位置的明智决定。
- Fitts's law can be used as an aid to make educated decisions on the size and placement of user interface elements.
- Fitts's law is centered around a mathematical equation that is used to illustrate the time it takes to reach a target object.
菲茨定律以数学方程式为中心,该数学方程式用于说明到达目标物体所需的时间。
- T Time is the amount of time required to complete the movement
是完成移动所需的时间- a is the human reaction time and b is the time needed by human nervous system to process a bit of information
a 是人类的反应时间,而 b 是人类神经系统处理一些信息所需的时间- D Distance is a measurement from the starting point to the end point (target object)
距离是从起点到终点(目标对象)的量度- W Width is the width of the target object
是目标对象的宽度
# Memory
How We Make Memories: Crash Course Psychology #13